India’s Space Programme Se-tenant Pair
Technical Data
| Stamp Set | India's Space Programme |
|---|---|
| Date of Issue | September 29, 2000 |
| Denomination | Rs. 6 |
| Quantity | 3,000,000 |
| Perforation | comb 13 x 13½ |
| Printer | Calcutta Security Printers Ltd |
| Watermark | No Watermark |
| Colors | Multicolor |
| Catalog Codes |
Michel IN 1784-1785 Stamp Number IN 1849 Yvert et Tellier IN 1550-1551 Stanley Gibbons IN 1953a |
| Themes | Astronauts | Flags | Globes | Outer Space | Space Traveling | Spacecraft |
Table of Contents
Indian Space Program and Commemorative Stamps
Overview:
India’s space program, formally organized in 1972 with the establishment of the Department of Space, has evolved into a significant contributor to global space technology. The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), National Remote Sensing Agency, and Physical Research Laboratory are key agencies in executing this program. The major systems include the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system and the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite (IRS) system.
Major Space Systems
- INSAT System:
- Purpose: Provides a wide range of services including telecommunications, broadcasting, meteorology, and disaster warning.
- Impact: The network supports over 800 TV transmitters, improving access to television for over 80% of India’s population. It also supports telecommunication terminals and has enhanced weather forecasting.
- IRS System:
- Purpose: Offers space-based remote sensing data for agriculture, water resources, urban development, and environmental monitoring.
- Impact: Key to projects involving drought and flood forecasting, mineral prospecting, and more.
Launch Vehicle Technology
- SLV-3 (Satellite Launch Vehicle):
- Capability: Initially put 40 kg class satellites into orbit.
- Progress: Evolved into more advanced vehicles like the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle (ASLV) and Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV).
- PSLV:
- Capability: Launches 1,200 kg class remote sensing satellites into polar sun-synchronous orbit.
- Significance: Known for its reliability and versatility in launching various satellites.
- GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle):
- Capability: Launches 2,000-2,500 kg class INSAT satellites into geosynchronous transfer orbit.
- Development: In advanced stages with a focus on increasing payload capacity and mission efficiency.
Space Science Research
- Institutes: Physical Research Laboratory, Space Physics Laboratory, Space Applications Centre, and ISRO Satellite Centre.
- Focus: Active research in space science and applications, aiming to advance our understanding of the universe and develop new technologies.
International Cooperation
- Agreements: India has cooperative agreements with several countries and space agencies.
- Training: Offers training to personnel from developing countries through the Sharing of Experience in Space (SHARES) program.
- Commercial Activities: Antrix Corporation handles space hardware and services for international customers.
Future Goals
- INSAT Services Expansion:
- Plans: Incorporate higher frequency transponders (KU and Ka-bands), and introduce new services such as direct-to-home television, tele-education, tele-health, and mobile communication.
- Advancements in Remote Sensing:
- Goals: Develop and launch more advanced satellites with improved spatial and spectral resolutions.
- Space Science Research:
- Aims: Expand research to contribute to global knowledge and open new avenues for Indian scientists.
Stamp Designs
- OCEANSAT-1 Stamp:
- Represents: The latest achievements in satellite technology related to ocean observation.
- INSAT-3B Stamp:
- Represents: Advances in telecommunications and broadcasting through INSAT.
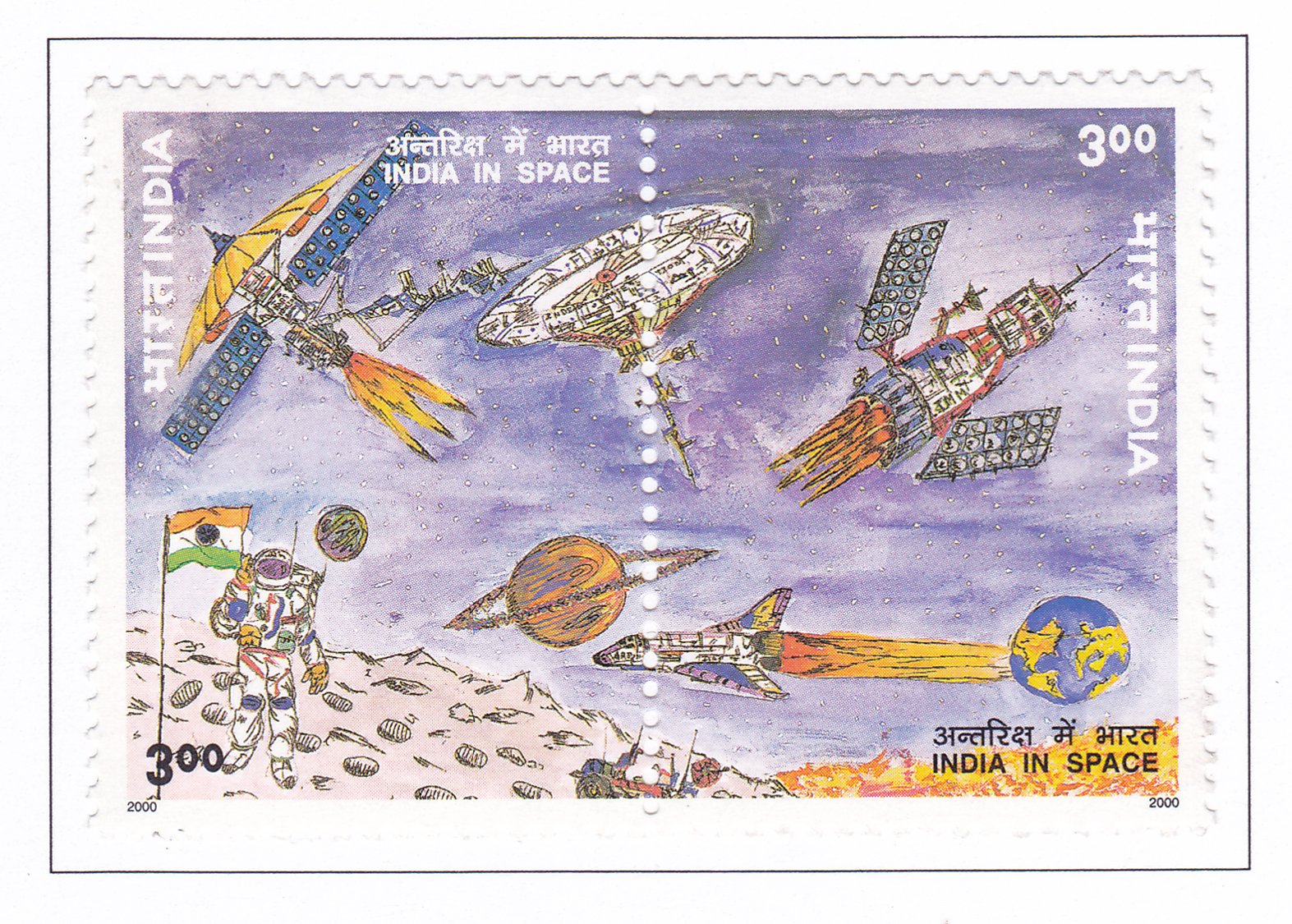
- Painting by S. Praveen:
- Theme: “India in Space-2025.”
- Significance: Reflects the fascination and aspirations of the younger generation for space exploration.
- First Day Cover:
- Artist: Parishi Minish Yagnik.
- Theme: “India in Space-2025.”
- Significance: Captures the vision and hopes for India’s future in space exploration.
These stamps and the associated first-day cover commemorate India’s achievements in space technology and reflect the country’s ambitious plans for the future.
